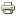
| Authority | Provision |
| TITLE I: OF THE NATION, OF THE STATE, OF ITS GOVERNMENT AND OF ITS FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES, CHAPTER IV: OF THE NATURAL RESOURCES, Article 14: Natural Resources |
Nonrenewable natural resources that are found in the territory and in the marine areas under national jurisdiction, genetic resources, biodiversity, and the radio-electric spectrum are national patrimony. |
| TITLE I: OF THE NATION, OF THE STATE, OF ITS GOVERNMENT AND OF ITS FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES, CHAPTER IV: OF THE NATURAL RESOURCES, Article 16: Protected Areas |
Wildlife, the conservation units that compose the National System of Protected Areas and the ecosystems and species that they contain constitute patrimonial assets of the Nation and are inalienable, imprescriptible, and not subject to seizure. The limits of the protected areas may only be reduced by law with the approval with two thirds of the votes of the members of the chambers of the National Congress. |
| TITLE I: OF THE NATION, OF THE STATE, OF ITS GOVERNMENT AND OF ITS FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES, CHAPTER IV: OF THE NATURAL RESOURCES, paragraph preceding Article 16 |
The high watersheds of the rivers and the zones of endemic, native and migratory biodiversity, are subjects of special protection by the public powers in order to guarantee their management and preservation as fundamental assets of the Nation. |
| TITLE I: OF THE NATION, OF THE STATE, OF ITS GOVERNMENT AND OF ITS FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES, CHAPTER IV: OF THE NATURAL RESOURCES, Article 17 Exploitation of natural resources (3) |
The preservation and reasonable exploitation of living and non-living resources from national marine areas, especially the joining of shoals and emersions within the national policy of marine development are declared a national priority |
| TITLE II: OF THE FUNDAMENTAL RIGHTS, GUARANTEES AND DUTIES, CHAPTER I: OF THE FUNDAMENTAL RIGHTS SECTION IV: OF THE COLLECTIVE RIGHTS AND OF THE ENVIRONMENT, Article 66: Collective and diffuse rights (1) |
The State recognizes collective and diffuse rights and interests, which are exercised with conditions and limitations established by law. Consequently, it protects: 1.The conservation of ecological balance, of fauna and flora. |
- Home
- Directory
-
Our Programs
-
Strategic Advocacy Course
- Collaborations
- Humane Education
- International Policy
-
Model Animal Welfare Act
- Get the Book!
- Contents
- Part 1: Guiding Principles - A Broad Overview
- Part 2: Proposal for the Wording of a New Animal Welfare Act
-
Part 3: Explanatory Notes
- Notes to Chapter 1: Preliminary Provisions
- Notes to Chapter 2: General Provisions
- Notes to Chapter 3: Keeping of Animals/Care of Animals
- Notes to Chapter 4: Specific Categories of Animal Use
- Notes to Chapter 5: Implementation and Enforcement Provisions
- Notes to Chapter 6: Penal and Final/Concluding Provisions
- Constitution Project
-
Strategic Advocacy Course
-
Resources
- Events
- About Us
- Blog
Don't miss out!
Subscribe to the World Animal Navigator to get monthly updates on our programs and resources! Browse past issues here.